Corrosion failure analysis and countermeasures of iron-based laser cladding layer (HY-industry technical centre)
As an important material surface modification technology, laser cladding mainly uses a high-energy density laser beam as a heat source to melt the alloy powder and the surface of the substrate at the same time, and after rapid solidification, it forms in situ with extremely low dilution and is formed into the substrate. The metallurgical bonding surface cladding layer significantly improves the wear resistance, corrosion resistance, heat resistance and oxidation resistance of the substrate surface, so as to achieve the purpose of surface modification. It has strong metallurgical bonding, excellent performance of the cladding layer, and no pollution to the environment. Etc. Laser cladding technology can not only remanufacture worn-out mechanical equipment to restore its performance, but also can strengthen the surface of new mechanical equipment and extend its service life. Therefore, laser cladding technology has gradually attracted people’s attention. Industrial applications in machinery, mining, petroleum and electric power industries. At present, commonly used laser cladding materials include iron-based, nickel-based, cobalt-based, ceramic composite materials, etc. Due to the variety of iron-based powders, good performance, and low cost, they are widely used in laser cladding. The quality of the iron-based laser cladding layer directly affects the effect of laser cladding on the surface of the equipment. In the actual use process, the iron-based laser cladding layer will be affected by factors such as laser cladding materials, processes, and environment. Failure in the form of wear, corrosion, etc. occurs.
Take hydraulic supports in the coal mining industry as an example. As a key equipment for mechanized coal mining, hydraulic supports mainly support and prevent coal gangue and coal dust from falling into the scraper conveyor and isolate the goaf. It is of great significance to coal mine safety. Due to the high humidity in the coal mine and the existence of a large amount of corrosive media, in order to reduce the corrosion failure of the hydraulic support and prolong the service life, the common method is to electroplating the surface of the hydraulic support movable column and cylinder body. As the country attaches importance to environmental protection, the electroplating industry is facing increasing pressure. The application of laser cladding technology to prepare iron-based cladding layers on the surfaces of hydraulic supports and cylinders is increasingly used. Based on this background, this article takes the movable column and cylinder of the hydraulic support as examples, mainly analyzes the corrosion failure of the iron-based laser cladding layer, and proposes a series of countermeasures.
-
Preparation of iron-based cladding layer
IGJR-4 type numerical control semiconductor laser cladding equipment is used to perform laser cladding treatment on the movable column and cylinder of the hydraulic support. The laser cladding material uses iron-based self-fluxing alloy powder. According to the performance requirements and working conditions of the movable column and cylinder surface of the hydraulic support, iron-based powders with different composition ratios are selected. The main process parameters of laser cladding are shown in Table 1.
Main parameters of laser cladding (Table 1) |
|||
Laser power(Kw) |
Laser cladding speedmm.min-1 |
Laser cladding overlap/mm |
Powder feeding/g.min-1 |
3~4 |
250~400 |
6~8 |
40~70 |
The main process of preparing the iron-based cladding layer of the movable column and cylinder body of the hydraulic support: cleaning→laser cladding→turning cladding layer→polishing cladding layer→quality inspection→finished product. For the old hydraulic support movable column and cylinder, the process of turning the fatigue layer is added before the beginning of the above process.
-
Corrosion failure analysis of iron-based laser cladding layer
In actual use, due to the unreasonable selection of laser cladding iron-based powder components and the mismatch of laser cladding process parameters, the iron-based laser cladding layer on the movable column and cylinder surface of the hydraulic support will inevitably suffer from corrosion failure. The commonly used corrosion failure analysis methods include appearance analysis, chemical composition analysis, microstructure analysis, and salt spray corrosion test analysis.
(1) Appearance analysis
Observe the iron-based cladding layer on the movable column and cylinder surface of the hydraulic support. When there are obvious defects such as pitting, rust, and corrosion pits, it indicates that the iron-based cladding layer has corroded and failed.
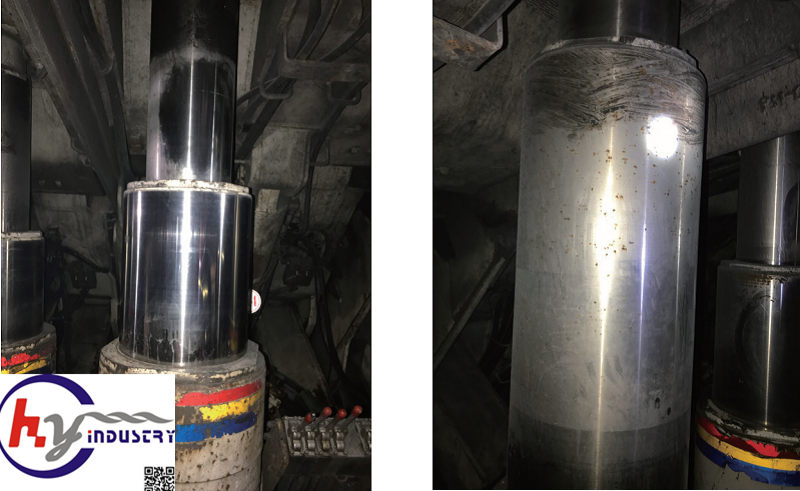

(2) Chemical composition analysis
Use a handheld X-ray fluorescence spectrometer to analyze the chemical composition of the iron-based laser cladding layer after laser cladding
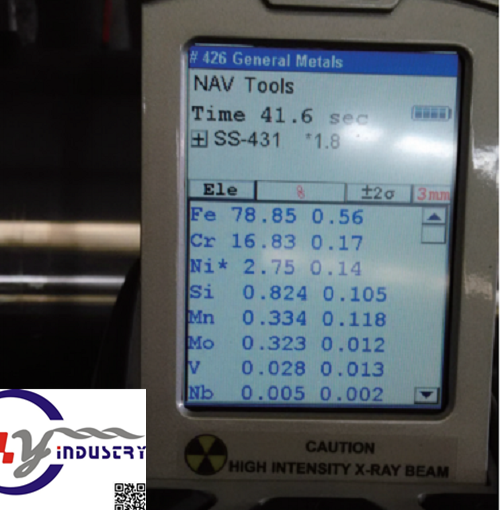 The handheld X-ray fluorescence spectrometer can directly measure the Cr content of the iron-based cladding layer. Since most of the mine environment where the movable column and cylinder of the hydraulic support are located contains corrosive media, in order to improve the performance of the hydraulic support, the movable pillar and the cylinder can be prepared by laser cladding technology to prepare a layer of iron-based cladding layer, but to ensure The corrosion resistance of the cladding layer is required. The cladding layer must contain enough Cr, so the laser cladding material used in laser cladding is high-Cr stainless steel iron-based self-fluxing powder. However, chromium carbide will precipitate at the grain boundaries of the microstructure of the cladding layer during the laser cladding process. When the Cr content is insufficient, a chromium-depleted area will appear, and the chromium-depleted area tends to be corroded preferentially, and the Cr content of the chromium-depleted area is similar. Lower than the uncorroded area. Therefore, a handheld X-ray fluorescence spectrometer was used to detect the Cr content of the iron-based cladding layer on the movable column and cylinder surface of the hydraulic support. By comparing the Cr content in different areas, the cause of the corrosion failure of the iron-based cladding layer was preliminarily judged.
The handheld X-ray fluorescence spectrometer can directly measure the Cr content of the iron-based cladding layer. Since most of the mine environment where the movable column and cylinder of the hydraulic support are located contains corrosive media, in order to improve the performance of the hydraulic support, the movable pillar and the cylinder can be prepared by laser cladding technology to prepare a layer of iron-based cladding layer, but to ensure The corrosion resistance of the cladding layer is required. The cladding layer must contain enough Cr, so the laser cladding material used in laser cladding is high-Cr stainless steel iron-based self-fluxing powder. However, chromium carbide will precipitate at the grain boundaries of the microstructure of the cladding layer during the laser cladding process. When the Cr content is insufficient, a chromium-depleted area will appear, and the chromium-depleted area tends to be corroded preferentially, and the Cr content of the chromium-depleted area is similar. Lower than the uncorroded area. Therefore, a handheld X-ray fluorescence spectrometer was used to detect the Cr content of the iron-based cladding layer on the movable column and cylinder surface of the hydraulic support. By comparing the Cr content in different areas, the cause of the corrosion failure of the iron-based cladding layer was preliminarily judged.
(3) Organizational analysis
An important reason for the corrosion failure of the iron-based laser cladding layer is the unreasonable process matching. To determine whether the corrosion failure is caused by the process, it is necessary to analyze the structure of the iron-based laser cladding layer. First prepare the metallographic observation sample of the iron-based laser cladding layer, the main process is sampling→grinding→polishing→corrosion, and then observe the metallographic structure with a metallurgical microscope.
The microstructure of the iron-based cladding layer mainly includes planar crystals and dendrites. At the junction between the bottom of the cladding layer and the interface, the ratio G/R of the temperature gradient (G) to the solidification rate (R) is the largest, and the structure is epitaxially grown in a planar crystal manner, while inside the cladding layer, it is mainly dendrites. Whether the matching of the laser cladding process is reasonable has a significant impact on the microstructure of the iron-based cladding layer. When the matching of the laser cladding process is reasonable, the microstructure of the iron-based cladding layer is mainly composed of flat crystals and dendrites with small dendrite sizes and relatively uniform distribution; when the matching of the laser cladding process is unreasonable, the iron-based cladding The microstructure of the layer is mainly composed of planar crystals and dendrites of different sizes. Because the grain boundaries are prone to segregation, and the potential at the grain boundaries is generally lower than the inside of the crystal grains, a micro-battery reaction occurs, which accelerates the occurrence of corrosion. It directly affects the morphology of the iron-based cladding layer, reduces the corrosion resistance of the cladding layer, and is more prone to failure during use.
(4) Salt spray corrosion test analysis
The failure analysis of the iron-based cladding layer can be judged by the salt spray corrosion test. Prepare the iron-based cladding layer salt spray corrosion test sample block, and conduct the salt spray test in accordance with the “Artificial Atmosphere Corrosion Test Salt Spray Test GB/T10125—2012”
-
Measures to reduce corrosion failure of iron-based laser cladding layer

